Semiconductor
Industry Challenges
Plastic encapsulation of IC components is a process where an integrated circuits chip is being capsulated with Epoxy Molding Compound (EMC) via the diverse molding process to prevent physical damage or corrosion. In addition to the complex chemorheology of EMC, the electronic components with sophisticated and fine design have brought the challenges and uncertainty to encapsulation processes. Common defects of chip encapsulation including incomplete voids, wire sweep, paddle shift and package warp
Moldex3D Solutions and Benefits
Moldex3D Chip Encapsulation provides comprehensive 3D solutions that help engineers to analyze the complicated physical phenomena inherent in encapsulation processes and further optimize the design and process. Moldex3D Chip Encapsulation provides innovative and complete tools for users to gain the sights of encapsulation processes. The filling and curing processes of the thermoset resins, along with all the critical characteristics including warpage, wire sweep and paddle shift can all be visualized by the software. From Moldex3D Chip Encapsulation, you can benefit from
■ Package and mold design validation and optimization to reduce manufacturing cost and design cycle time.
■ Simulation-driven-design of complex fluid-structure interactions and innovative IC packages during molding process.
Moldex3D Solves Tough Problems
Incomplete voids
The IC industry is always challenging for thinner packages with smaller footprint. Though the flip-chip technology has various advantages over the other high-density electronic packaging approaches, there are rising challenges to ensure moldability and minimize defects with rapid advances in flip chip technology such as decreasing bump pitch, stand-off height, thinner package profiles and molded materials.
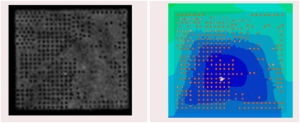
Moldex3D filling analysis can be used to optimize the process to reduce defects without doing actualexperiments involving a large DOE matrix. The filling simulation can effectively reduce the design toimplementation cycle time, identifying key problems before actual fabrication. And diverse molding process such as molded underfill, capillary underfill and compression molding processes can be analyzed through the simulation tools.
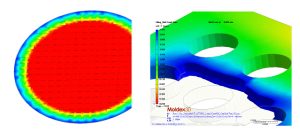
Wire sweep / Paddle shift
During the fabrication of epoxy molding compound in IC encapsulation process, stress-induced problems such as wire sweep and paddle shift are the most common problems. The viscous drag force on wires exerted by the resin melt flow causes wire sweep, while non-uniform force loading on paddle results in paddle shift.
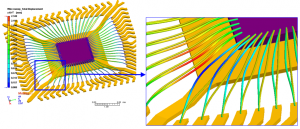
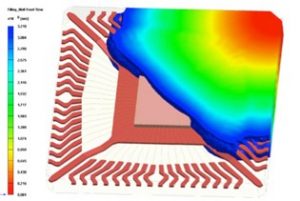
In figure, the position of wire cross over is shown in a closer look. In the wire crossover display, the shape of wires are shown as deformed mesh on true scale, and wires contact each other will be marked in red, while other wires remain theirs original color.
Moldex3D provides wire sweep prediction and wire sweep index for user to determine if the setting of In figure, the position of wire cross over is shown in a closer look. In the wire crossover display, the shape of wires are shown as deformed mesh on true scale, and wires contact each other will be marked in red, while other wires remain processing conditions, the selection of materials, and lead frame layout is appropriate. And the integrated paddle shift analysis can help connect filling and structure analyses and post-process, which gives a comprehensive solution for paddle shift phenomenon.
Post mold cure
During the post mold cure process, the volume of EMC will shrink due to the effect of cross-linking and undergo the stress relaxation due to viscoelastic behavior. In addition, because of the fact that the coefficient of thermal expansion of each element in the encapsulated unit is different, a warpage issue will have a high probability to occur in this process as well. If the warpage problem is too severe, the internal microstructure of the encapsulated unit might be damaged, cracked, or malfunctioned.
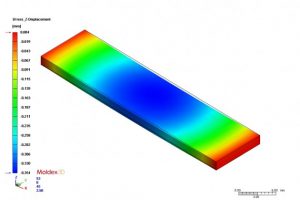
The Z-displacement when the IC unit is removed from the oven to room temperature at the end of the post-mold cure process. The simulation of the final warpage is 0.354 mm, which is very close to the experiment result.
Moldex3D’s post-mold cure analysis provides comprehensive simulation results that allow users to predict potential deformation problems. Moldex3D can provide an accurate prediction of the final warpage analysis by considering the variations in the way warpage changes with temperature and curing degree at the constant pressure during the entire post-mold curing process, meaning from the time the unit is put into the oven to when it is cooled to room temperature.