Stress
- Stress analysis is a fundamental aspect of material science and engineering, focusing on the distribution of internal forces within materials and structures.
- Stress analysis plays a crucial role in designing and optimizing structures to ensure their mechanical integrity, product quality and performance,
- Fluid-structure interaction (FSI): analysis the shift or deformation behavior like part inserts, core shift, paddle shift
- Fiber orientation and weld line effect:mechanical property analysis to predict on strength enhance or reduction
- Viscoelastic effect: It can be applied to the residual stress distribution of annealing, product deformation, and optical analysis
- Geometric nonlinear analysis: for the buckle behavior of plastic parts that are prone to warp
- For more information, please refer to the stress webpage
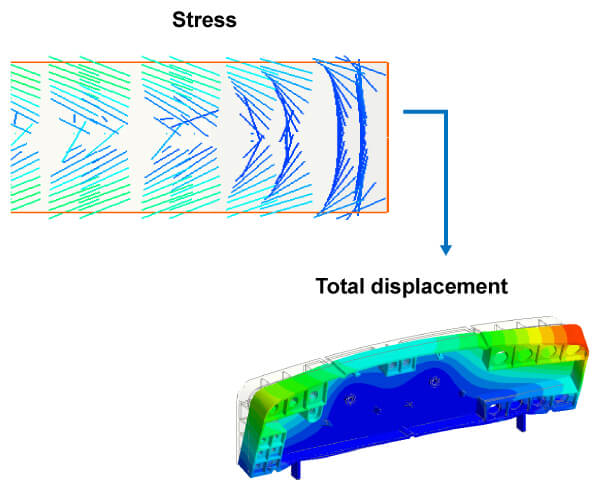
Why Stress Analysis
Stress analysis has been mainly applied for designers to observe stress distribution inside parts and part inserts. The stress distribution has a significant impact on part quality and structural strength, influenced by many molding factors, including temperature, force, part shape and size, material properties, etc. The stress over safety loading may destroy structural strength and cause breakage on the part. Therefore, obtaining accurate stress analysis results upfront is crucial for designers to reduce fatigue failure and extend product life cycle.
Challenges
- Visualize stress and displacement distributions of parts and part inserts
- Evaluate plastic displacements under certain external loadings
- Evaluate mechanical strength around welding line region
- Evaluate structure resistance in consideration with fiber orientation effect
What Can Moldex3D Stress Do?
- Predict potential deformation problems to evaluate material properties and process conditions
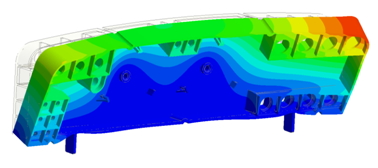
Consider welding line effect to provide more accurate prediction on strength reduction
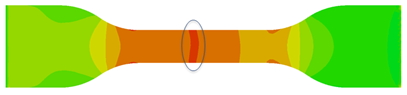
Severe necking phenomenon can be observed in Z-displacement contour figure
- Consider fiber orientation effect that will affect shrinkage and part strength
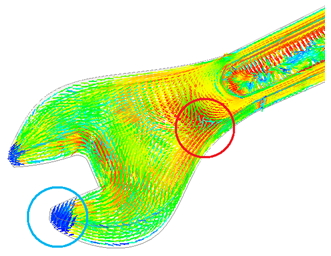
(a) Blue circle: randomly oriented; (b) Red circle: highly oriented Fiber orientation distribution
- Predict the displacement of inserts due to non-uniform flow-induced pressure with accurate 2-way Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) consideration for Core Shift behavior of MCM, as well as Wire Sweep and Paddle Shift behaviors of IC Packaging
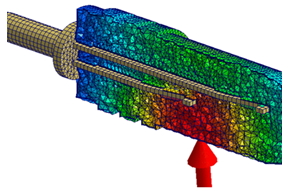
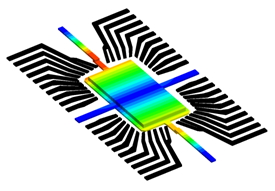
Applicable Industries
- Electronics
- Automotive
- Medical
- Consumer Product
- IC Packaging
Applicable Moldex3D Package
- Moldex3D eDesign Package
- Moldex3D Professional Package
- Moldex3D Advanced Package